Page 41 - IJSA, Vol. 4, No 2, 2021
P. 41
International Journal of Science Annals, Vol. 4, No. 2, 2021
рrint ISSN: 2617-2682; online ISSN: 2707-3637; DOI:10.26697/ijsa
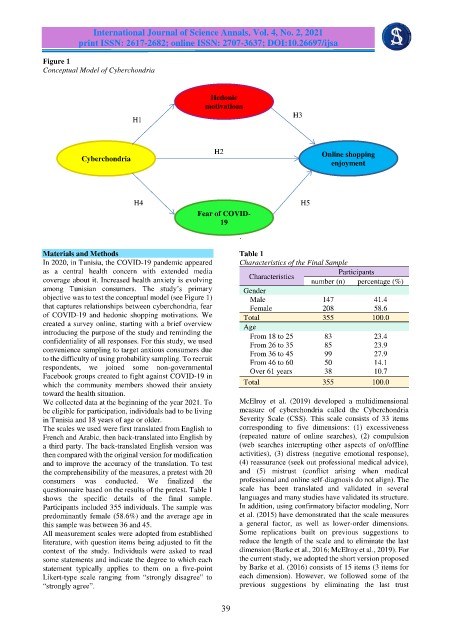
Figure 1
Conceptual Model of Cyberchondria
Hedonic
motivations
H3
H1
H2
Cyberchondria Online shopping
enjoyment
H4 H5
Fear of COVID-
19
.
Materials and Methods Table 1
In 2020, in Tunisia, the COVID-19 pandemic appeared Characteristics of the Final Sample
as a central health concern with extended media Participants
coverage about it. Increased health anxiety is evolving Characteristics number (n) percentage (%)
among Tunisian consumers. The study’s primary Gender
objective was to test the conceptual model (see Figure 1) Male 147 41.4
that captures relationships between cyberchondria, fear Female 208 58.6
of COVID-19 and hedonic shopping motivations. We Total 355 100.0
created a survey online, starting with a brief overview Age
introducing the purpose of the study and reminding the From 18 to 25 83 23.4
confidentiality of all responses. For this study, we used From 26 to 35 85 23.9
convenience sampling to target anxious consumers due From 36 to 45 99 27.9
to the difficulty of using probability sampling. To recruit From 46 to 60 50 14.1
respondents, we joined some non-governmental Over 61 years 38 10.7
Facebook groups created to fight against COVID-19 in
which the community members showed their anxiety Total 355 100.0
toward the health situation.
We collected data at the beginning of the year 2021. To McElroy et al. (2019) developed a multidimensional
be eligible for participation, individuals had to be living measure of cyberchondria called the Cyberchondria
in Tunisia and 18 years of age or older. Severity Scale (CSS). This scale consists of 33 items
The scales we used were first translated from English to corresponding to five dimensions: (1) excessiveness
French and Arabic, then back-translated into English by (repeated nature of online searches), (2) compulsion
a third party. The back-translated English version was (web searches interrupting other aspects of on/offline
then compared with the original version for modification activities), (3) distress (negative emotional response),
and to improve the accuracy of the translation. To test (4) reassurance (seek out professional medical advice),
the comprehensibility of the measures, a pretest with 20 and (5) mistrust (conflict arising when medical
consumers was conducted. We finalized the professional and online self-diagnosis do not align). The
questionnaire based on the results of the pretest. Table 1 scale has been translated and validated in several
shows the specific details of the final sample. languages and many studies have validated its structure.
Participants included 355 individuals. The sample was In addition, using confirmatory bifactor modeling, Norr
predominantly female (58.6%) and the average age in et al. (2015) have demonstrated that the scale measures
this sample was between 36 and 45. a general factor, as well as lower-order dimensions.
All measurement scales were adopted from established Some replications built on previous suggestions to
literature, with question items being adjusted to fit the reduce the length of the scale and to eliminate the last
context of the study. Individuals were asked to read dimension (Barke et al., 2016; McElroy et al., 2019). For
some statements and indicate the degree to which each the current study, we adopted the short version proposed
statement typically applies to them on a five-point by Barke et al. (2016) consists of 15 items (3 items for
Likert-type scale ranging from “strongly disagree” to each dimension). However, we followed some of the
“strongly agree”. previous suggestions by eliminating the last trust
39