Page 25 - IJSA, Vol. 4, No 2, 2021
P. 25
International Journal of Science Annals, Vol. 5, No. 1-2, 2022
рrint ISSN: 2617-2682; online ISSN: 2707-3637; DOI:10.26697/ijsa
Based on the obtained results, it was established that for The smallest specific weight for group 3 respondents is
group 1 of respondents (cadets), the most important the following psychogenies: the coronavirus pandemic
factors of mental trauma are the risk of death of and romantic relationship problems, which do not
relatives, family (42.61%), separation from relatives, exceed 5-6%.
family (25.22%), and problems of adaptation to a new The significance of the problems of living in a new place
place of residence (16.52%). for the respondents of groups 1 (42.06%) and 2
For group 2 of respondents (students who are in the (16.52%) is explained by a certain uncertainty of the
territory of Ukraine and beyond), problems of situation regarding the duration of the war in Ukraine
adaptation to a new place of residence are relevant and the deterioration of the life quality in the new place.
(42.06%), separation from relatives, family (28.04%), The relevance of problems with communication with
problems with communication with friends/relatives friends/relatives for groups 2 (25.23%) and 1 (15.65%)
(25.23%). is caused both by their significance for respondents and
At the same time, for group 3 respondents (students the importance of communication using mobile and
located in Kharkiv region), the indicators of mental Internet communication for young people in general. It
trauma were higher than other groups and included the is related to the dissemination of socially significant
following: personal safety risk (61.90%), lack of work information, which is a cognitive resource in the process
or other source of income (37.14%), fear of death and of forming ideas, opinions, value orientations and
risk of property loss (37.86%). The high specific weight adequate behavior. Therefore, the violation of mobile
of vital psychogenia among the respondents of group 3 and Internet communication after the Russian shelling
is explained by the complex military-humanitarian of Ukraine is always perceived sensitively by the youth.
situation and essentially inhuman conditions of Further detailing of symptoms of mental trauma was
existence in Kharkiv and the region (daily rocket carried out using the DASS-21 tool.
attacks, frequent stays in shelters, lack of light, water Manifestations of anxiety among the KNUIA cadets and
and heat in some areas, deaths and injuries of the students in the war and martial law conditions are shown
population from shelling and anti-personnel mines, etc.). in Figure 2.
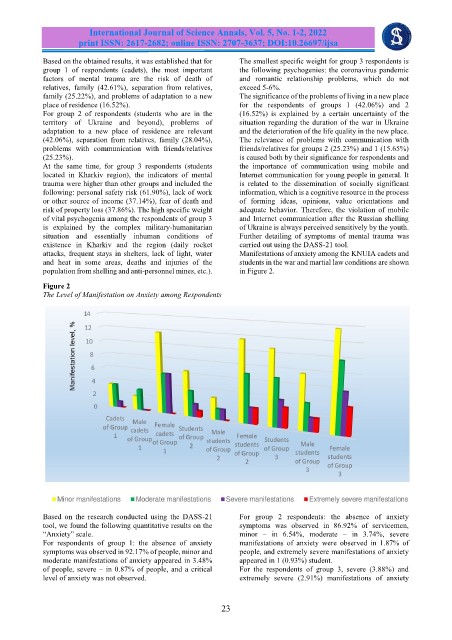
Figure 2
The Level of Manifestation on Anxiety among Respondents
Based on the research conducted using the DASS-21 For group 2 respondents: the absence of anxiety
tool, we found the following quantitative results on the symptoms was observed in 86.92% of servicemen,
“Anxiety” scale. minor – in 6.54%, moderate – in 3.74%, severe
For respondents of group 1: the absence of anxiety manifestations of anxiety were observed in 1.87% of
symptoms was observed in 92.17% of people, minor and people, and extremely severe manifestations of anxiety
moderate manifestations of anxiety appeared in 3.48% appeared in 1 (0.93%) student.
of people, severe – in 0.87% of people, and a critical For the respondents of group 3, severe (3.88%) and
level of anxiety was not observed. extremely severe (2.91%) manifestations of anxiety
23