Page 9 - IJSA, Vol. 1, No 1-2, 2018
P. 9
Vol. 1, No. 1-2, 2018 IJSA
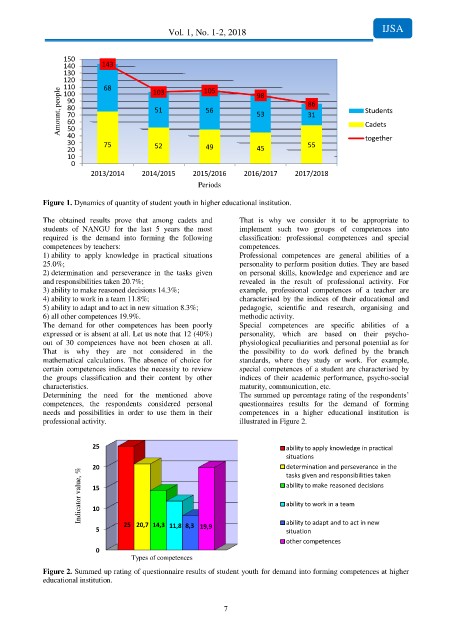
150
140 143
130
120 68 103 105 98
110
Amount, people 90 51 56 53 86 Students
100
80
70
31
60
Cadets
50
40
30 75 55 together
20 52 49 45
10
0
2013/2014 2014/2015 2015/2016 2016/2017 2017/2018
Periods
Figure 1. Dynamics of quantity of student youth in higher educational institution.
The obtained results prove that among cadets and That is why we consider it to be appropriate to
students of NANGU for the last 5 years the most implement such two groups of competences into
required is the demand into forming the following classification: professional competences and special
competences by teachers: competences.
1) ability to apply knowledge in practical situations Professional competences are general abilities of a
25.0%; personality to perform position duties. They are based
2) determination and perseverance in the tasks given on personal skills, knowledge and experience and are
and responsibilities taken 20.7%; revealed in the result of professional activity. For
3) ability to make reasoned decisions 14.3%; example, professional competences of a teacher are
4) ability to work in a team 11.8%; characterised by the indices of their educational and
5) ability to adapt and to act in new situation 8.3%; pedagogic, scientific and research, organising and
6) all other competences 19.9%. methodic activity.
The demand for other competences has been poorly Special competences are specific abilities of a
expressed or is absent at all. Let us note that 12 (40%) personality, which are based on their psycho-
out of 30 competences have not been chosen at all. physiological peculiarities and personal potential as for
That is why they are not considered in the the possibility to do work defined by the branch
mathematical calculations. The absence of choice for standards, where they study or work. For example,
certain competences indicates the necessity to review special competences of a student are characterised by
the groups classification and their content by other indices of their academic performance, psycho-social
characteristics. maturity, communication, etc.
Determining the need for the mentioned above The summed up percentage rating of the respondents’
competences, the respondents considered personal questionnaires results for the demand of forming
needs and possibilities in order to use them in their competences in a higher educational institution is
professional activity. illustrated in Figure 2.
25 ability to apply knowledge in practical
situations
determination and perseverance in the
20
Indicator value, % 15 ability to make reasoned decisions
tasks given and responsibilities taken
ability to work in a team
10
25 20,7 14,3 11,8 8,3 19,9 ability to adapt and to act in new
5 situation
other competences
0
Types of competences
Figure 2. Summed up rating of questionnaire results of student youth for demand into forming competences at higher
educational institution.
7